Echocardiography: A Comprehensive Guide
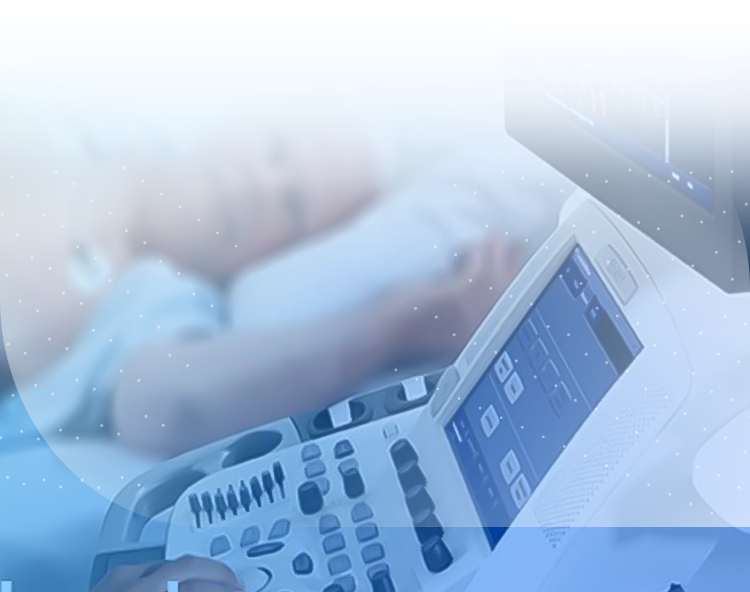
chocardiography (Ultrasound Echocardiography) is a non-invasive imaging technique used to assess the structure and function of the heart. This method uses sound waves to create images of the heart and blood vessels, providing important information about the heart’s condition. In this article, we will explore the types of echocardiography, how it is performed, its applications, and the benefits of this method.
- Types of Echocardiography
Echocardiography is divided into several types:
-
Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE): This is the most common type of echocardiography, performed by placing a probe on the chest. This method is suitable for a general assessment of the heart and blood vessels.
-
Transesophageal Echocardiography (TEE): In this method, the probe is inserted into the esophagus to obtain more detailed and clearer images of the heart and blood vessels. This method is typically used when TTE does not provide sufficient results.
-
Stress Echocardiography: This type of echocardiography helps assess heart function under stress conditions (usually through exercise or medication). This method can help identify coronary artery diseases.
-
Three-Dimensional Echocardiography: This type of echocardiography creates three-dimensional images of the heart, helping physicians better visualize cardiac structures.
- How Echocardiography is Performed
Echocardiography is usually performed as follows:
-
Preparation: The patient typically lies down. Anesthesia is not required, and the patient can remain awake during the procedure.
-
Probe Placement: The physician applies a special gel to the skin of the patient’s chest and places the probe on it. This gel aids in the transmission of sound waves.
-
Imaging: The probe sends sound waves to the heart and receives the echoes of these waves. These echoes are converted into images of the heart.
-
Image Analysis: The physician analyzes the obtained images and examines information related to the size, shape, and function of the heart.
- Applications of Echocardiography
Echocardiography is used for the diagnosis and assessment of various heart diseases, including:
-
Valvular Diseases: Evaluating the function of heart valves and identifying valve insufficiency or stenosis.
-
Cardiac Muscle Diseases: Such as cardiomyopathy and heart failure.
-
Coronary Artery Diseases: Identifying problems caused by arterial blockages.
-
Congenital Heart Disorders: Assessing the structure of the heart in newborns and children.
-
Preoperative Care: Evaluating the heart’s condition before cardiac surgeries.
- Benefits of Echocardiography
-
Non-invasive: Echocardiography is a non-invasive method that does not require surgery or entry into the body.
-
No Side Effects: This method has no specific side effects due to the use of sound waves and the absence of X-rays.
-
High Accuracy: Echocardiography can provide accurate information about the structure and function of the heart.
-
Real-time Capability: This method allows for the observation of heart movements in real time.
- Conclusion
Echocardiography is a key tool in the diagnosis and assessment of heart diseases, providing valuable information about the function and structure of the heart. Given its non-invasive nature and high accuracy, this method is recognized as one of the primary techniques in cardiovascular medicine.